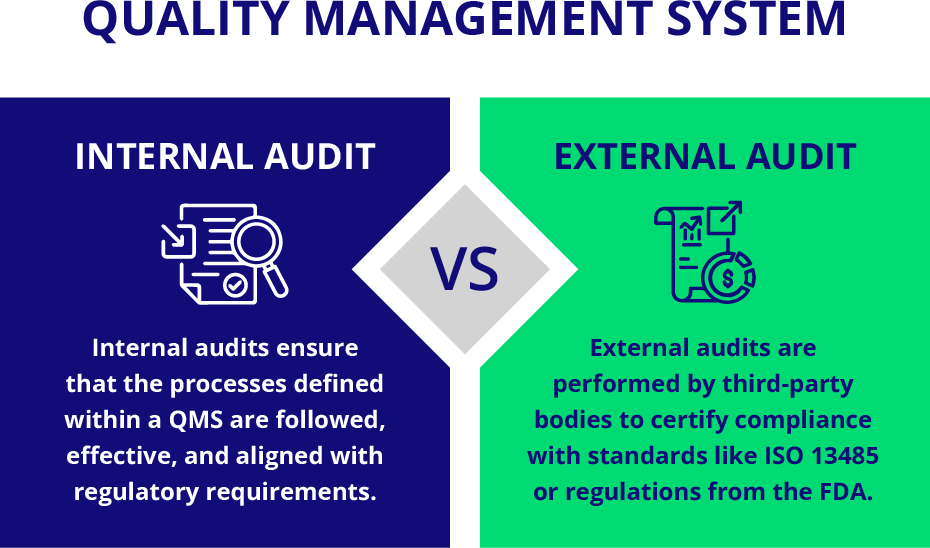
Quality Management Systems (QMS) form the backbone of compliance and efficiency in regulated industries like medical devices. Internal audits play a critical role in maintaining and improving these systems. Internal audits ensure that the processes defined within a QMS are followed, effective, and aligned with regulatory requirements. Internal audits are non-negotiable for companies that aim to keep their operations smooth and compliant.
Comparison with External Audits
While internal audits focus on evaluating processes from within, external audits are performed by third-party bodies to certify compliance with standards like ISO 13485 or FDA regulations. Internal audits, as a proactive measure, ensure readiness before an external audit. By identifying gaps internally, companies can avoid costly surprises during external assessments, giving you a sense of preparedness and control.
What is an Internal Audit?
Internal audits are systematic evaluations of an organization’s operations, internal controls, and risk management processes. In the context of a QMS, these audits assess the effectiveness of the processes that form the system, identify gaps or non-conformities, and drive continuous improvement.
The purpose of an internal audit is to ensure that processes meet both internal goals and regulatory requirements. Internal audits provide insight into potential risks, inefficiencies, and areas where the organization can enhance compliance and performance.
Types of Internal Audits
Internal audits within a QMS can be broken down into:
- Product Audits: Focused on ensuring that products meet specified requirements.
- Process Audits: Evaluate specific processes within the QMS for compliance and efficiency.
- System Audits: Assess the overall effectiveness of the QMS in meeting quality objectives.
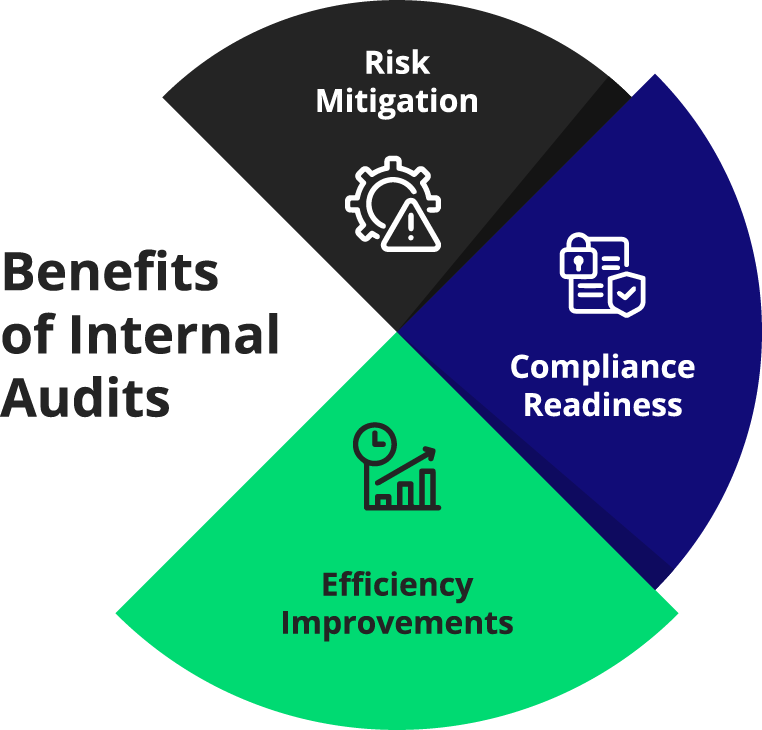
What are the Benefits of Conducting Regular Internal Audits?
Conducting regular internal audits delivers numerous benefits to an organization, including:
Identify Gaps and Enhance QMS
Regular audits help pinpoint non-conformities and areas for process improvement. This proactive approach ensures that issues are addressed before they affect product quality or compliance.
Prepare for External Audits
Internal audits prepare organizations for external assessments by identifying potential areas of concern. This readiness can significantly reduce the time and resources needed during external audits and increase the likelihood of a positive outcome.
Mitigating Risks and Improving Compliance
Internal audits can help organizations identify potential risks before they materialize into compliance issues. Addressing these risks helps maintain continuous compliance, minimizing the likelihood of penalties or recalls.
Boosting Efficiency and Customer Satisfaction
Internal audits can refine processes and lead to more streamlined operations, directly improving efficiency. This, in turn, enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring that products meet or exceed quality standards.
The Audit Process
The internal audit process involves a systematic review of the QMS to ensure that it functions effectively and complies with standards like ISO 13485. This process includes preparation, conducting the audit, documenting findings, and following up with corrective actions.
Phases of the QMS Internal Audit Process
- Preparation:
- Develop an audit plan that includes the objectives, scope, and criteria.
- Gather the necessary documentation, such as procedures and records, for review.
- Schedule the audit to ensure the availability of resources and minimize disruption.
- Conducting the Audit:
- Perform interviews with staff, observe processes in action, and review documentation to verify compliance.
- Assess the effectiveness of processes and identify areas that require attention.
- Reporting Findings:
- Document audit findings in a clear and detailed report, categorizing non-conformities and areas for improvement.
- Present the report to management to ensure transparency and facilitate informed decision-making.
- Follow-Up and Corrective Actions:
- Work with relevant departments to implement corrective actions based on audit findings.
- Verify that corrective actions are effective and that non-conformities have been resolved.
Common Audit Findings
- Non-Conformities: Major or minor instances where processes do not meet set requirements.
- Opportunities for Improvement: Areas where processes can be optimized for better performance.
- Observations: Findings that, while not non-conformities, may pose a risk if not addressed.
Key Objectives of QMS Internal Audits
The primary objectives of conducting internal audits within a QMS include:
Process Conformity Assessment
Internal audits evaluate whether each process adheres to internal procedures and external regulatory requirements, ensuring consistency and reliability.
Performance Evaluation
Audits assess key performance indicators (KPIs) to determine how well processes meet quality objectives. This helps in adjusting processes to achieve better outcomes.
QMS Implementation Verification
The audits verify that all aspects of the QMS are fully implemented across departments, ensuring the system functions as intended.
Driving Compliance and Continuous Improvement
Internal audits are not just about compliance, they are a key driver of continuous improvement. They encourage a culture of compliance and excellence by identifying new opportunities to enhance processes, keeping you motivated and forward-thinking.
Planning for an Effective QMS Internal Audit
Proper planning is essential to a successful internal audit. A well-structured plan ensures that audits align with organizational goals and are conducted effectively.
Developing an Audit Plan
- Goal Setting: Define the primary objectives of the audit and the insights you expect to gain.
- Scope and Schedule: Determine the processes and departments to be audited and create a timeline.
- Resources and Tools: Use audit checklists, documentation, and software tools to ensure thorough evaluation.
Establishing Clear Audit Objectives
Clear objectives guide the audit, focusing on critical areas such as compliance with ISO 13485 and identifying process inefficiencies. Specific goals can streamline the audit process and support readiness for external audits.
The Role of the Internal Audit Team
An effective internal audit team is essential for providing objective evaluations that drive improvements within the QMS.
Training Internal Auditors
Ongoing training ensures that internal auditors remain current with regulatory updates and best practices, maintaining the quality of the audit process.
Responsibilities of the Internal Auditor
- Assessment and Analysis: Evaluate processes through interviews, document reviews, and observations.
- Maintaining Independence: Auditors must remain objective to ensure their assessments are unbiased.
- Reporting to Top Management: Communicating audit findings and recommendations to leadership ensures that issues are addressed promptly.
Stay Audit-ready
At RookQS, we offer expert internal audit support to ensure your audits are thorough and effective. Our team will assess your compliance, identify areas for improvement, and help strengthen the effectiveness of your Quality Management System (QMS).
Partner with RookQS
Reach out to schedule a consultation today. Let’s ensure your QMS remains audit-ready and aligned with all regulatory requirements.
