CE Mark
The CE Mark emerged from the European Union’s initiative to create a single market with the free movement of goods, services, people, and capital. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, the EU introduced directives to harmonize national standards across member states. Key milestones include:
New Approach Directives (1985): Simplified the regulatory environment and harmonized safety and performance requirements.
Single European Act (1987): Laid the groundwork for the single European market, eliminating trade barriers.
Implementation (1993): Made CE Marking mandatory for specific product categories, aligning with the EU’s single market agenda.
The primary objectives of CE Marking are to ensure the free movement of goods, enhance consumer safety, promote fair competition, and facilitate market surveillance. The regulatory framework includes legislative measures, harmonized standards, essential requirements, conformity assessment procedures, the Declaration of Conformity (DoC), technical documentation, and market surveillance.
What is the CE Mark?
The CE Mark is a certification mark that signifies a product’s conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards within the European Economic Area (EEA). The letters “CE” stand for “Conformité Européenne,” meaning “European Conformity” in French. The primary objective of the CE Mark is to facilitate free trade within the EEA by ensuring that products meet uniform safety, health, and environmental standards.
What is the Importance of the CE Mark?
The CE Mark is crucial for market access, consumer trust, and legal compliance in the European market. Products bearing the CE Mark can move freely across EEA member states without needing additional local certifications, provided they comply with the CE marking requirements. This mark indicates that a product conforms to essential EU requirements, promoting consumer safety and fair competition.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework for CE marking includes:
- New Approach Directives: Simplifies the regulatory environment and ensures harmonized safety and performance requirements across the EU.
- Harmonized Standards: Provides the technical specifications needed to demonstrate conformity.
- Conformity Assessment Procedures: Outlines the steps manufacturers must take to show compliance.
- Declaration of Conformity (DoC): This document confirms that a product meets all relevant EU requirements.
- Technical Documentation: Includes detailed information on the product’s design, manufacturing process, and compliance evidence.
How to Obtain CE Marking
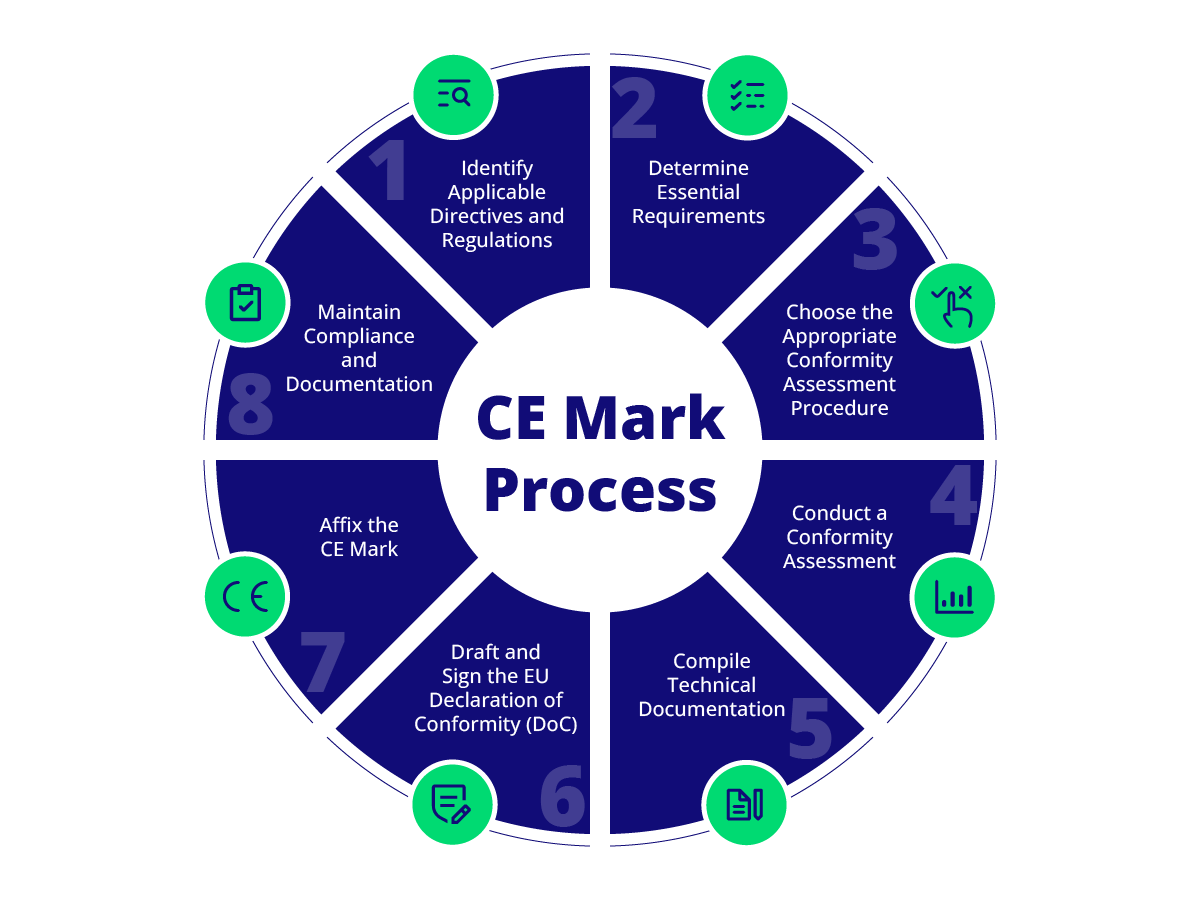
Identify Applicable Directives and Regulations
Determine which EU directives and regulations apply to your product category. This step ensures that you address all relevant requirements for your product.
Determine Essential Requirements
Identify the essential requirements that your product must meet to comply with EU standards. This includes health, safety, and environmental protection criteria.
Choose the Appropriate Conformity Assessment Procedure
Select the appropriate conformity assessment procedure based on the product’s risk level. Options include self-assessment for lower-risk products or third-party assessment by a Notified Body for higher-risk products.
Conduct a Conformity Assessment
Perform the necessary conformity assessment, which may involve testing, inspection, and quality assurance processes.
Compile Technical Documentation
Prepare comprehensive technical documentation, including a general product description, design and manufacturing information, risk assessments, and test reports.
Draft and Sign the E
U Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
Create and sign the DoC, declaring that your product complies with all applicable European regulations.
Affix the CE Mark
After meeting all criteria, apply the CE Mark to your product in a way that is clear, readable, and permanent.
Maintain Compliance and Documentation
Regularly review and update your product’s technical documentation and ensure ongoing compliance with EU regulations.
CE Mark Certification Vs. Self-Declaration
Choosing between self-declaration and third-party certification depends on the product’s risk level and applicable EU directives. Self-declaration is suitable for lower-risk products and offers a cost-effective and quicker route to CE marking. Third-party certification provides an added layer of verification and is mandatory for higher-risk products. Both processes require manufacturers to ensure and document compliance with EU standards.
Steps to CE Marking
- Find the CE Directive(s) that Apply to Your Product: Consult EU resources like the European Commission website and the NANDO database.
- Know the Essential Requirements for Your Product: Determine the specific requirements by reading relevant directives and harmonized standards.
- Determine if You Need Third-Party Certification: Identify if your product requires assessment by a Notified Body, especially for higher-risk products.
- Create and Maintain Technical Documentation: Prepare and keep comprehensive technical documentation to support your product’s conformity.
EU Declaration of Conformity
The EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC) is a critical document asserting that a product complies with applicable EU regulations. It ensures traceability, accountability, and transparency. A valid DoC is necessary to affix the CE Mark.
Legal Implications
Misusing the CE Mark can lead to serious legal consequences, including fines, product recalls, and market access restrictions. Manufacturers, importers, and distributors must strictly comply with EU directives to avoid penalties and maintain consumer trust.
High-Risk Products and CE Marking
For high-risk products like medical devices, achieving CE marking involves stringent regulatory requirements, comprehensive technical documentation, and often the involvement of Notified Bodies. Ensuring compliance with these standards is essential for market access and public safety.
Learn More About CE Mark Certification
Discover how to navigate the CE Marking process with Rook Quality Systems, your
Medical Device Quality Consultants.
Additional Resources and Further Reading
- European Commission – Single Market Compliance Space: provides guidance, ensuring compliance with EU single market regulations.
- European Commission – Market surveillance for products: explains the importance and implementation of market surveillance in the EU.
- EUR-Lex – The Official Journal of the European Union
European Commission – CE Marking: provides information on the CE marking, its significance, and the responsibilities of manufacturers, importers, and distributors.